Biometric Authentication: The Future of Digital Security
Biometrics Unveiled: A Revolutionary Approach to Authentication
In an era dominated by digital interactions and the constant evolution of technology, the need for robust and secure authentication methods has never been more critical. Biometric authentication, with its ability to provide a unique and personal identification based on physiological or behavioral traits, is emerging as the future of digital security. This article explores the transformative impact of biometric authentication and its role in shaping the landscape of digital security.
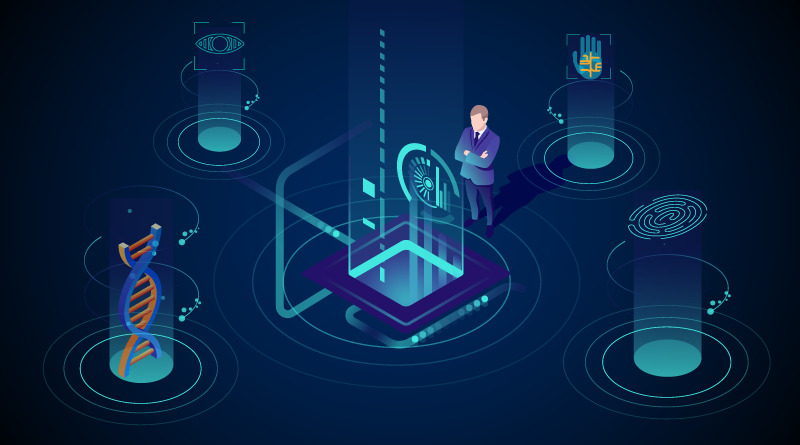

The Rise of Biometric Authentication:
- Enhanced Security Measures:
Biometric authentication offers a higher level of security compared to traditional methods such as passwords or PINs. The use of unique biological traits, such as fingerprints, facial features, or iris patterns, adds an additional layer of protection, making it significantly harder for unauthorized access. - User Convenience:
Biometric authentication simplifies the user experience by eliminating the need to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens. The ease of use, combined with the speed of identification, enhances user convenience, making it a preferred choice for both consumers and businesses. - Reducing Identity Theft:
Traditional authentication methods are susceptible to identity theft through password breaches or unauthorized access. Biometric data, being inherently unique to each individual, minimizes the risk of identity theft, providing a more secure environment for sensitive information. - Multi-Modal Authentication:
The future of biometric authentication lies in multi-modal approaches, combining multiple biometric identifiers for heightened security. Integrating fingerprints with facial recognition or voice authentication creates a more comprehensive and reliable authentication system.. - Integration with IoT Devices:
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, biometric authentication is becoming integral to securing connected devices. From smartphones to smart homes, the seamless integration of biometrics adds an extra layer of protection to personal and sensitive data.
Challenges and Solutions:
- Privacy Concerns:
The collection and storage of biometric data raise privacy concerns. To address this, robust encryption methods and adherence to strict privacy regulations are essential. Transparent policies on data usage and storage help build trust among users. - Spoofing and Forgery:
Biometric systems are not immune to spoofing attempts, where attackers use forged biometric data to gain unauthorized access. Advanced biometric technologies, such as liveness detection and anti-spoofing measures, are continuously evolving to counter such threats. - Standardization and Interoperability:
The lack of standardized biometric authentication protocols can hinder interoperability between systems. Establishing industry standards and protocols ensures compatibility and a seamless experience across different platforms and devices.

In Conclusion
Biometric authentication is undeniably at the forefront of the future of digital security. Its ability to balance enhanced security with user convenience makes it a compelling choice for individuals and organizations alike. As technology continues to advance, the ongoing refinement of biometric solutions will play a pivotal role in creating a secure and seamless digital environment. Embracing biometric authentication not only enhances security but also paves the way for a future where the protection of digital identities is more robust than ever before.